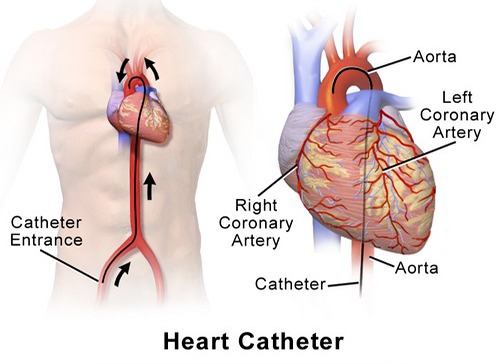
Data from the ALPACA Phase II trial reveal that lepodisiran, an siRNA therapy, reduced Lp(a) levels by nearly 94% up to six months with a single dose. The results, offered at ACC 2025 and published in the New England Journal of Medicine, mark a potential breakthrough in treating stubborn genetic cardiovascular risk.